How are aluminum PCB boards manufactured?
Date:2024-04-09 02:30:35
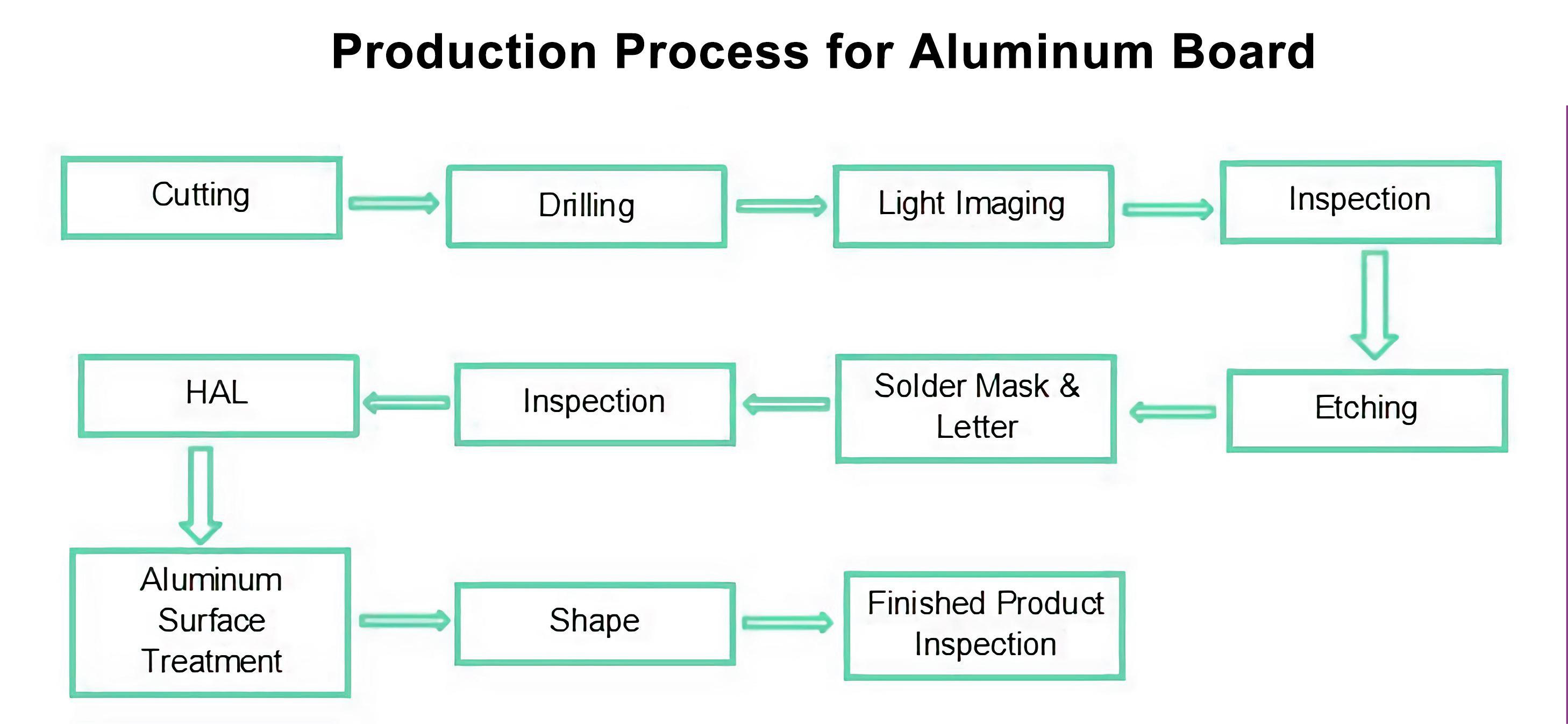
Aluminum PCB boards, also known as metal core PCBs (MCPCBs), are specialized printed circuit boards designed for applications requiring efficient heat dissipation and enhanced thermal management. The manufacturing process for aluminum PCB boards involves several intricate steps to ensure the proper construction and functionality of the final product. In this article, we will delve into the detailed process of manufacturing aluminum PCB boards.
1. Substrate Selection:
The manufacturing process begins with the selection of the aluminum substrate. The substrate serves as the foundation of the PCB and provides the necessary thermal conductivity for heat dissipation. High-quality aluminum sheets are chosen based on their thickness, surface finish, and thermal properties.
2. Cleaning and Surface Preparation:
The aluminum substrate undergoes a thorough cleaning process to remove any contaminants, oils, or residues that may interfere with the adhesion of the subsequent layers. Surface preparation techniques such as etching or abrasive blasting may be employed to enhance surface roughness and promote better adhesion.
3. Dielectric Layer Application:
A dielectric layer is applied to the surface of the aluminum substrate to provide electrical insulation between the metal core and the copper traces. The dielectric material, typically composed of a thermally conductive epoxy resin or polyimide, is evenly coated onto the substrate using techniques such as spray coating, screen printing, or lamination.
4. Copper Foil Lamination:
Thin copper foil sheets are laminated onto both sides of the dielectric layer to form the conductive traces of the PCB. The copper foil is bonded to the substrate using heat and pressure, ensuring a strong and reliable connection. The thickness of the copper foil is carefully controlled to meet the design requirements of the PCB.

5. Circuit Patterning:
The desired circuit patterns and traces are created on the copper foil using a photolithography process. A photoresist material is applied to the copper surface, followed by exposure to UV light through a mask with the desired circuit pattern. The exposed areas of the photoresist are then developed and etched away, leaving behind the copper traces.
6. Through-Hole Drilling:
Holes are drilled through the PCB to allow for component mounting and electrical connections between layers. Specialized drilling equipment with high precision is used to create holes of varying diameters according to the design specifications. The drilled holes are then cleaned and prepared for subsequent processes.
7. Plating and Surface Finishing:
The exposed copper surfaces and drilled holes are plated with additional layers of metal to improve conductivity and protect against oxidation. Common plating materials include tin, nickel, and gold. Surface finishes such as HASL (hot air solder leveling), ENIG (electroless nickel immersion gold), or OSP (organic solderability preservative) may be applied to enhance solderability and corrosion resistance.
8. Component Assembly:
Surface mount components and through-hole components are assembled onto the PCB using automated pick-and-place machines or manual soldering techniques. Solder paste is applied to the pads, and the components are placed onto the aluminum PCB board with high precision. The assembly is then subjected to reflow soldering or wave soldering to secure the components in place.
9. Testing and Quality Assurance:
The assembled PCB undergoes rigorous testing and inspection to ensure functionality, reliability, and compliance with specifications. Various tests, including electrical continuity tests, functional tests, and thermal performance tests, are conducted to verify the integrity of the PCB. Any defects or anomalies are identified and rectified to maintain the highest quality standards.Final Inspection and Packaging:Once testing is completed, the finished PCBs are subjected to final inspection to ensure they meet the required quality standards. PCBs that pass inspection are cleaned, labeled, and packaged according to customer specifications. Protective packaging materials are used to safeguard the PCBs during transportation and storage.
Conclusion:
The manufacturing process of aluminum PCB boards involves a series of precise and controlled steps to create high-quality printed circuit boards with efficient thermal management capabilities. By carefully selecting materials, applying advanced manufacturing techniques, and conducting thorough testing and inspection, manufacturers can produce aluminum PCB boards that meet the demanding requirements of various industries and applications.
