How Do Rigid PCB Factories Ensure Quality Control?
Date:2025-01-07 10:50:48
Rigid PCB (Printed Circuit Board) manufacturing plays a critical role in the electronics industry. These components are essential in everything from smartphones and computers to medical devices and automotive systems. With the growing demand for high-performance electronics, ensuring the highest quality in the production process is paramount for rigid PCB suppliers and rigid PCB manufacturers. But how do these factories guarantee that the final product meets stringent quality standards? Let’s take a closer look at the rigorous quality control processes involved in rigid PCB manufacturing.
1. Material Inspection and Selection
The first step in quality control for rigid PCB manufacturers is the careful selection of raw materials. The quality of the base materials used, such as copper foils, fiberglass, and resin, significantly influences the overall performance of the PCB. High-quality materials are sourced from trusted suppliers to avoid any defects in the final product.Before any manufacturing begins, rigid PCB suppliers perform thorough inspections of the incoming materials. These materials are checked for consistency, thickness, and purity, as any variation could result in subpar electrical conductivity or mechanical properties. The materials are also tested for resistance to temperature and humidity, ensuring the durability of the final PCB in different environments.
2. Design and Prototyping Review
Before moving on to mass production, rigid PCB manufacturers often create prototypes to test design specifications. During this phase, design engineers use advanced software tools to simulate and analyze the design’s performance, checking for potential flaws such as electrical shorts, signal interference, or excessive heat. These designs are carefully reviewed and optimized for performance, manufacturability, and reliability.By using computer-aided design (CAD) and electronic design automation (EDA) tools, rigid PCB suppliers ensure that each layer, trace, and via is positioned with precision. Any issues uncovered during prototyping, such as poor routing or alignment errors, are corrected before production begins.
3. Automated Manufacturing Processes
Once the design is approved, the manufacturing process begins. Modern rigid PCB manufacturing involves a mix of automated and manual steps. Automation helps achieve high precision and consistency in large-scale production runs. Automated machines are used for tasks like drilling holes, cutting copper traces, and applying layers of solder mask.For example, automated optical inspection (AOI) systems are commonly used to detect any defects during the assembly process. These machines use cameras to capture high-resolution images of the PCB and compare them with the design specifications to detect irregularities like misalignment, missing components, or poor solder joints. AOI systems offer fast and accurate detection, ensuring that defects are identified before moving to the next stage of production.
4. Electroplating and Solder Mask Application
In rigid PCB manufacturing, electroplating is used to deposit a thin layer of metal, such as copper, onto the board to create conductive pathways. This process must be meticulously controlled to ensure uniformity, as variations in thickness could lead to weak spots or potential failure points.The application of the solder mask is another critical stage where quality control plays a vital role. The solder mask prevents oxidation and ensures that soldering will only occur at designated pads. To achieve precise solder mask application, manufacturers use a combination of high-precision screens and automated processes to ensure an even coat and prevent defects like bubbles, scratches, or misalignment.
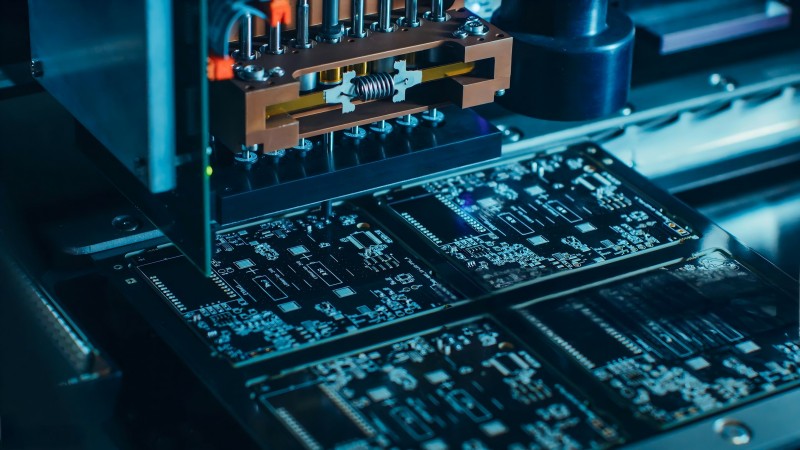
5. Electrical Testing
After the PCB is assembled, the next step in quality control is electrical testing. Rigid PCB manufacturers use various testing methods to check whether the board performs as expected. One of the most common methods is the In-Circuit Test (ICT), where the PCB is placed into a testing machine that checks for continuity, shorts, and correct voltages across the board. This ensures that the PCB’s electrical pathways function correctly before further assembly.Functional testing is also carried out, particularly for complex or high-frequency PCBs. Here, the board is tested in real-world conditions to ensure it performs its intended tasks effectively. This can include testing signal integrity, power distribution, and thermal performance. Any board that fails these tests is rejected and either reworked or discarded.
6. Environmental and Stress Testing
To ensure the rigid PCB can withstand extreme conditions, environmental stress tests are also conducted. These include temperature cycling tests (testing the PCB at high and low temperatures), vibration testing, and humidity testing. The goal is to ensure that the PCB can operate reliably in various environments and is resistant to degradation over time.In addition, rigid PCB suppliers and manufacturers also test for resistance to mechanical stresses. This includes checking the board for flexibility, strength, and durability, ensuring that it will not crack or warp under normal use.

7. Final Inspection and Packaging
Once the rigid PCBs have passed all the tests, a final visual inspection is conducted to ensure that there are no visible defects such as scratches, dents, or chips. Inspection teams use both manual and automated methods to check for cosmetic issues before the boards are packaged for shipment.Rigid PCB suppliers often include detailed documentation with the product, including test reports and certifications to prove that the board meets specific industry standards such as IPC-A-600 (Acceptability of Printed Boards) or IPC-2221 (Generic Requirements for Designing Printed Boards). The packaging is also designed to protect the PCBs from environmental factors like moisture, dust, and static during transit.
Quality control in rigid PCB manufacturing is a multifaceted process that involves careful material selection, precise design, automated testing, and continuous improvement. By focusing on each stage of production, rigid PCB manufacturers and rigid PCB suppliers ensure that they deliver reliable, high-performance PCBs that meet the needs of industries worldwide. Through the use of advanced technologies, testing methods, and consistent monitoring, these manufacturers maintain the high standards necessary to support the ever-evolving electronics industry.
