What is pcb assembly process?
Date:2024-03-28 00:20:13
PCB assembly, also known as printed circuit board assembly, is a critical step in the manufacturing of electronic devices. It involves assembling various electronic components onto a printed circuit board (PCB) to create a functional electronic assembly. The PCB assembly process encompasses several stages, each of which plays a crucial role in producing high-quality electronic assemblies. In this article, we'll delve into the PCB assembly process, exploring its key stages, components, and considerations.
Introduction to PCB Assembly
PCB assembly is a complex process that requires precision, expertise, and attention to detail. It involves assembling electronic components such as resistors, capacitors, integrated circuits (ICs), and connectors onto a PCB, following a specific layout or design. The assembled PCB serves as the foundation for electronic devices ranging from consumer electronics to industrial equipment and aerospace systems.
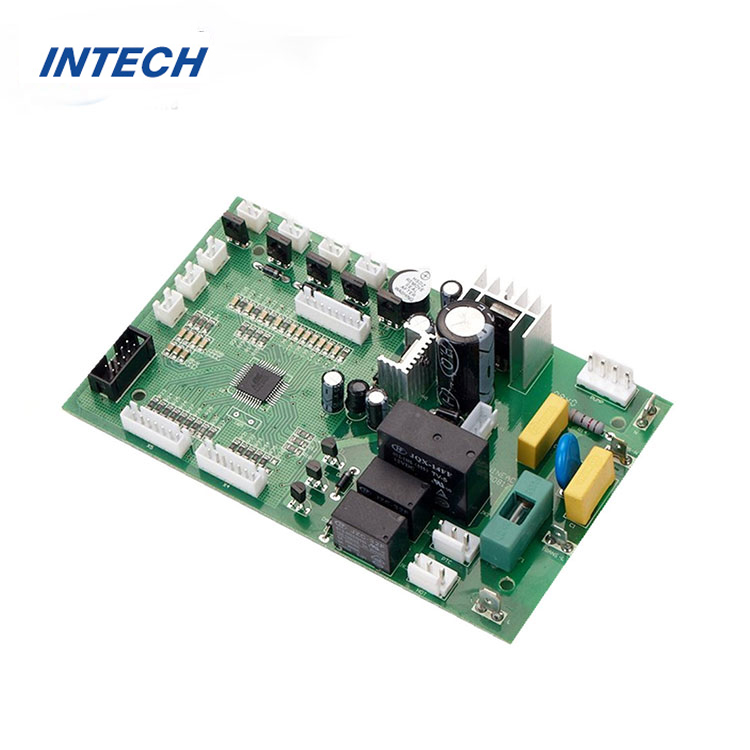
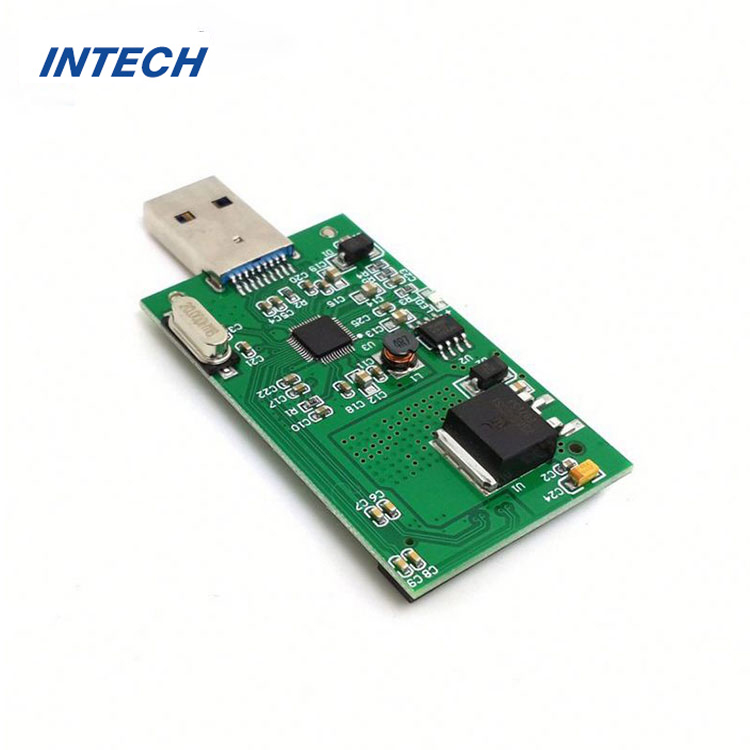
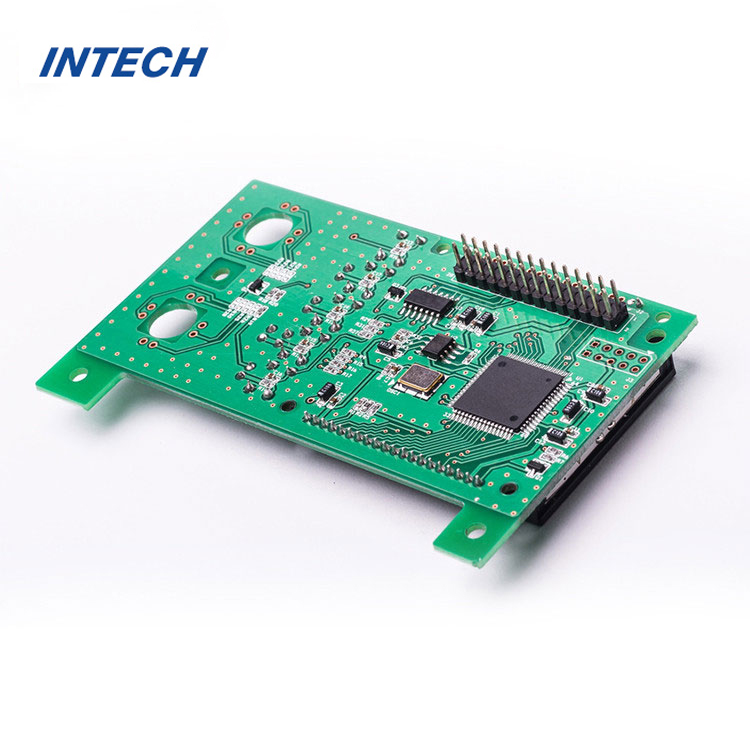


Key Stages of the PCB Assembly Process
PCB Fabrication: The PCB assembly process begins with the fabrication of the PCB itself. This involves etching a copper-clad laminate substrate to create the desired circuit pattern, followed by drilling holes for component mounting and applying solder mask and silkscreen layers for protection and identification.
Component Procurement: Once the PCBs are fabricated, the next step is to procure the electronic components needed for assembly. Component procurement involves sourcing components from reputable suppliers, verifying their quality and specifications, and ensuring their availability for the assembly process.
Component Placement: During component placement, electronic components are placed onto the PCB according to the design layout or bill of materials (BOM). Automated pick-and-place machines are often used to accurately position components onto the PCB, optimizing efficiency and accuracy.
Solder Paste Application: Solder paste is applied to the pads on the PCB using a stencil or solder paste dispenser. The solder paste serves as a temporary adhesive that holds the components in place during the soldering process and facilitates the formation of solder joints.
Reflow Soldering: Reflow soldering is the primary method used to attach components to the PCB. The assembled PCB is passed through a reflow oven, where the solder paste is heated to a precise temperature, causing it to melt and form solder joints between the components and the PCB pads.
Inspection and Testing: After reflow soldering, the assembled PCB undergoes inspection and testing to ensure that all components are properly mounted and soldered. Automated optical inspection (AOI) and X-ray inspection are commonly used to detect defects such as misalignment, solder bridging, and insufficient solder joints.
Cleaning: Once the PCB assembly has been inspected and tested, it may undergo cleaning to remove any flux residues or contaminants left over from the soldering process. Cleaning is typically performed using specialized cleaning agents and equipment to ensure the cleanliness and reliability of the assembly.
Final Testing and Quality Assurance: After cleaning, the assembled PCB undergoes final testing and quality assurance procedures to verify its functionality, performance, and reliability. Functional testing, electrical testing, and environmental testing may be performed to ensure that the PCB meets all specifications and requirements.
Considerations in PCB Assembly
Component Compatibility: Ensuring that all components are compatible with the PCB design and assembly process is essential for successful PCB assembly.
Quality Control: Implementing robust quality control measures throughout the assembly process helps identify and rectify any issues or defects early on, ensuring the reliability and performance of the assembled PCBs.
Regulatory Compliance: Compliance with regulatory standards and requirements, such as RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and IPC (Association Connecting Electronics Industries) standards, is essential for ensuring the safety, reliability, and environmental sustainability of PCB assemblies.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the PCB assembly process is a multifaceted undertaking that involves several stages, each of which contributes to the creation of functional and reliable electronic assemblies. From PCB fabrication and component procurement to component placement, soldering, inspection, and testing, every step in the process requires precision, expertise, and attention to detail. By understanding the intricacies of the PCB assembly process and adhering to best practices and quality standards, manufacturers can produce high-quality PCB assemblies that meet the needs and specifications of various industries and applications.
