Custom PCB: Key Considerations
Date:2024-09-20 14:32:03
Printed circuit boards (PCBs) play a crucial role in modern electronic devices, serving as the backbone that connects various electronic components. The quality of a pcb circuit board directly impacts a product's performance and reliability. Therefore, understanding key considerations is essential when customizing PCBs. Here are several important factors to focus on during the process.
Basic Overview of PCBs
A PCB, or printed circuit board, is a board used to mechanically support and electrically connect electronic components through conductive pathways printed onto an insulating substrate. It typically consists of multiple layers, including copper traces (conductive pathways), an insulating base, and a silkscreen layer to label component positions. Complex designs may involve multiple layers to meet high-density wiring needs.
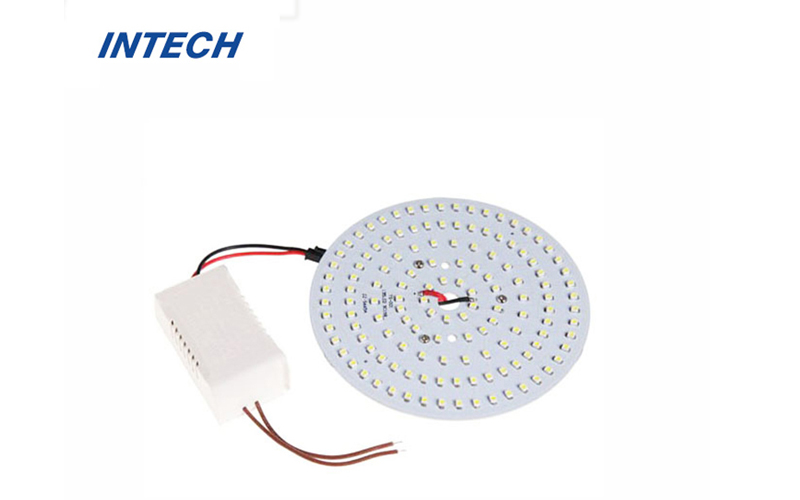

Preparations Before Customizing a PCB
Clearly Define Design Requirements
- Application: Different applications (such as consumer electronics, industrial control systems, and medical devices) have varying performance demands for PCBs. It’s important to identify the specific requirements for your application.
- Size and Shape: Choose the appropriate custom pcb size and shape based on the space limitations of the device. For certain designs, non-standard shapes may be necessary.
- Layers: Depending on the circuit's complexity and the need for signal integrity, decide whether to use a single-layer, double-layer, or multi-layer PCB.
Circuit DesignUse professional pcb board design software (such as Altium Designer or Eagle) to plan the layout and routing, ensuring electrical performance and signal quality. Be sure to conduct a pcb board design rule check (DRC) to prevent issues like shorts or overly small spacing.
Material Selection
- Substrate Material: FR-4 is the most commonly used material, but for special needs like heat resistance or cost optimization, other materials such as Rogers or aluminum-based boards may be chosen.
- Copper Thickness: Choose the appropriate copper thickness based on the current-carrying requirements of your design.
Key Considerations During the Customization Process
Choosing a Reliable ManufacturerEvaluate the manufacturer’s qualifications, experience, customer feedback, and sample quality. Ensure that they have the production capacity and quality control standards to meet your needs.
File Preparation and CommunicationPrepare comprehensive manufacturing documentation, including Gerber files, assembly drawings, and bill of materials (BOM). Communicate clearly with the manufacturer about the design details. Confirm specific manufacturing processes, such as surface treatment (e.g., gold plating, tin plating, OSP) and drilling specifications.
Sample ValidationBefore mass production, produce and test a sample to verify the accuracy of the design. Identifying and correcting issues early helps avoid costly mistakes during full-scale production.
Cost and Lead Time ManagementUnderstand the breakdown of the quote, and be mindful of additional charges such as expedited delivery or special material fees. Negotiate reasonable delivery times with the manufacturer, balancing cost and efficiency.
Conclusion:
Customizing a PCB is a complex process involving multiple stages, from design to production. Every step requires careful planning, from defining design needs and selecting materials to choosing a reliable manufacturer. Ensuring thorough communication and validating samples are key to successfully customizing a high-quality PCB.
